In the fields of information security and OSINT, crt.sh has long been considered a foundational tool. It is widely used for subdomain discovery, infrastructure analysis, and monitoring SSL/TLS certificate issuance. Despite its minimalistic interface, the service is built on top of one of the most important internet security mechanisms – Certificate Transparency.
What is crt.sh?
crt.sh is a web-based service that allows users to search and analyze SSL/TLS certificates published in Certificate Transparency (CT) logs. It aggregates data from public CT logs and makes it possible to see which certificates have been issued for a specific domain or organization.
In simple terms: if a publicly trusted SSL certificate has ever been issued for a domain, there is a very high chance that it can be found via crt.sh.
A quick overview of Certificate Transparency
Certificate Transparency is an open framework that requires Certificate Authorities (CAs) to publish all issued public SSL/TLS certificates into publicly accessible logs. These logs are append-only and cryptographically verifiable, which means existing records cannot be silently altered.
The main goal of CT is to detect mistakenly issued or malicious certificates and to make certificate issuance transparent. This allows domain owners, researchers, and browser vendors to monitor certificates and improve trust across the web.
Certificate Transparency was introduced as a security standard to address the risk of unauthorized or fraudulent certificate issuance. By making all publicly trusted certificates visible, CT enables independent monitoring by domain owners, security researchers, and browser vendors, significantly increasing accountability across the public PKI ecosystem.
crt.sh is the most commonly used tool for browsing and auditing these CT logs.
How certificate data ends up in crt.sh
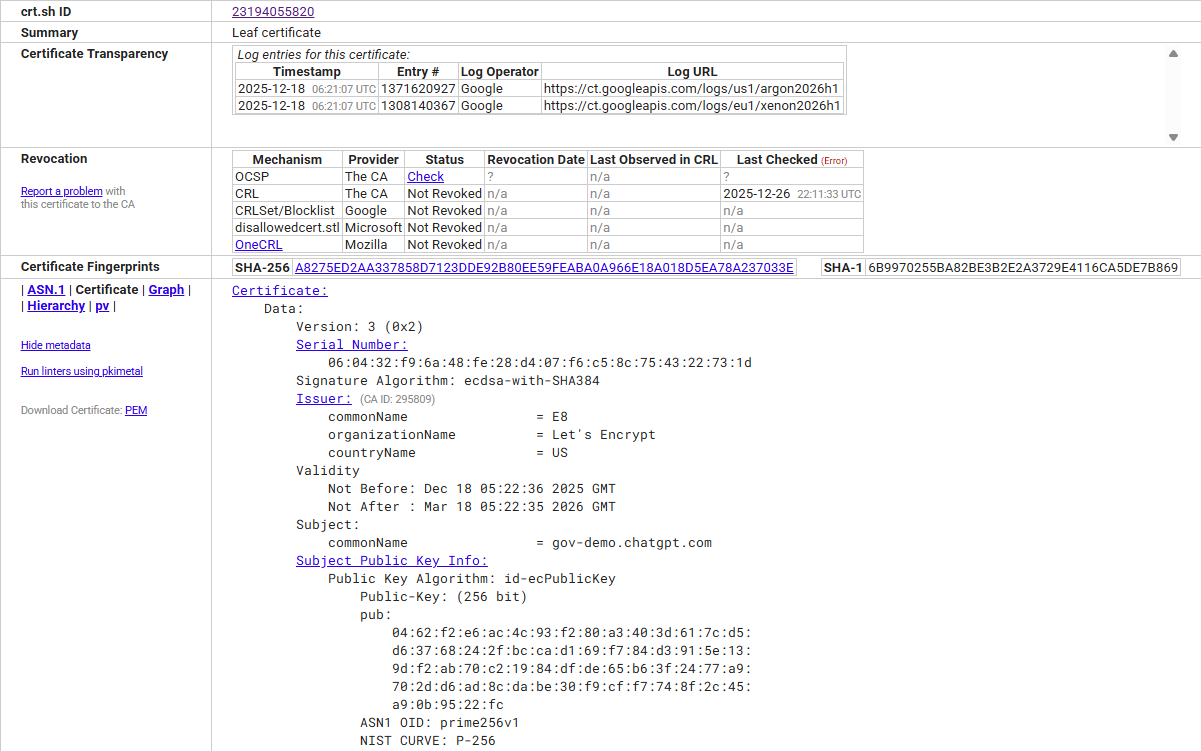
Behind crt.sh is a PostgreSQL-based indexing system operated by Sectigo that continuously monitors public Certificate Transparency logs. Every time a Certificate Authority (CA) issues a new publicly trusted certificate and submits it to the CT ecosystem, this information becomes available to crt.sh.
These CT logs are public, append-only data structures that store essential certificate details such as the subject, issuing CA, validity period, and – most importantly – the domain names covered by the certificate. As a result, crt.sh can be used to discover subdomains and related services that are protected by TLS, even if they are not easily discoverable through DNS brute forcing or traditional search engines.
Key features of crt.sh
Searching certificates by domain
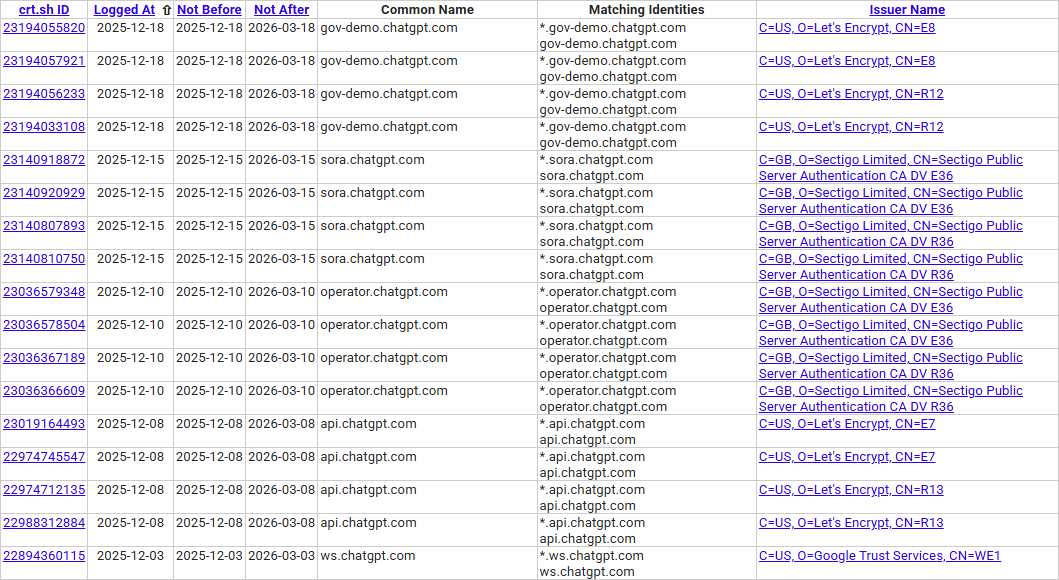
The primary use case of crt.sh is searching certificates by domain name.
For example, a search for example.com will return certificates issued not only for the main domain, but also for its subdomains such as www.example.com, mail.example.com, and others.
This is why crt.sh is often described as one of the most popular subdomain discovery sources.
Certificate details and analysis
Each certificate entry provides detailed technical information, including:
- issue date and expiration date
- issuing Certificate Authority
- certificate owner (Subject)
- list of domains and subdomains from the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) field
- cryptographic algorithms and parameters
- SHA-1 and SHA-256 fingerprints
This data can reveal hidden relationships between domains, CDN usage, internal environments, and forgotten services.
Additional search options
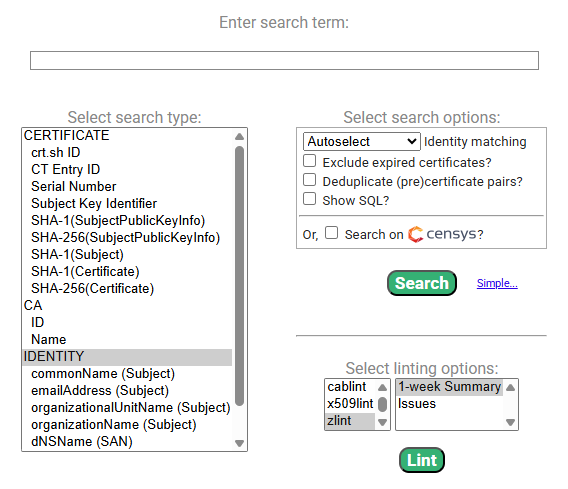
Beyond domain-based searches, crt.sh supports queries by:
- organization name
- email address included in the certificate
- certificate fingerprint
- internal
crt.shID
This makes the service useful not only for administrators, but also for security analysts, penetration testers, and incident response teams.
Practical use cases
crt.sh is commonly used for:
- OSINT and reconnaissance – discovering subdomains and infrastructure
- Security audits – verifying proper certificate issuance
- Domain monitoring – detecting unauthorized certificates
- Incident response – investigating certificate-related security events
Basic access to crt.sh is completely free and does not require registration, which further contributes to its popularity in the security community.
Limitations to keep in mind
It is important to understand that crt.sh:
- only contains publicly trusted certificates
- does not guarantee that discovered subdomains are currently active
- is not a real-time scanner – results depend on CT log updates
Even with these limitations, crt.sh remains an extremely valuable source of intelligence.
Why crt.sh matters
crt.sh is a simple yet powerful tool that plays a key role in modern OSINT, infrastructure analysis, and SSL/TLS monitoring. It clearly demonstrates the value of Certificate Transparency and how public data can significantly improve internet security.
Recently, new services working with Certificate Transparency data have started to appear. However, most of them are still in an early stage, with relatively small certificate databases, and cannot yet compete with mature and well-established tools like crt.sh.